Home
Noticias
Referentes científicos de nuestro entorno para un nuevo 11 de febrero
El IMB-CNM centra sus actividades del Día Internacional de la Mujer y la Niña en la Ciencia en una campaña pública de visibilización de sus investigadoras. En el ámbito de las escuelas, se han coordinado charlas divulgativas en seis localidades diferentes
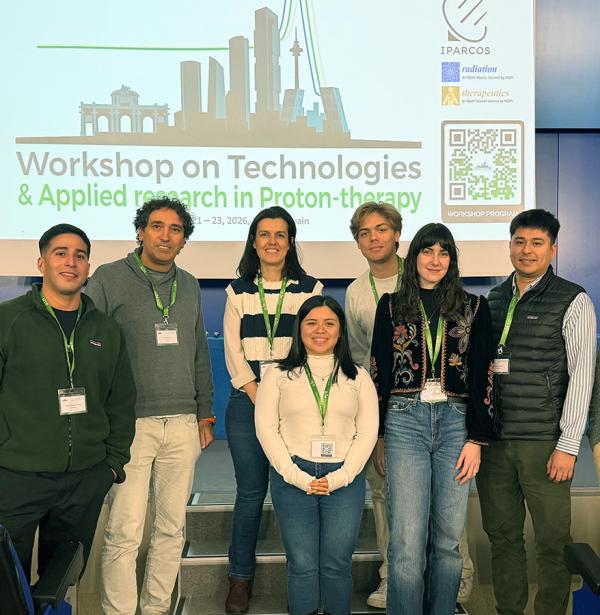
Fuerte presencia del IMB-CNM en el Workshop de Terapia de Protones celebrado en Madrid
El personal investigador predoctoral y posdoctoral presentó múltiples avances del IMB-CNM en tecnología de detectores, lo que valió dos premios a la Mejor Ponencia
Agenda
Highlights
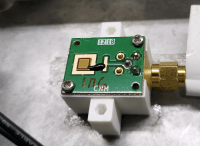
Accurate neutron detection in mixed photon-neutron and pulsed radiation fields is technically challenging, impacting industrial and medical applications. This paper presents the first measurements of thermal neutrons in conventional radiotherapy accelerators using a silicon carbide (SiC) P–N diode with different neutron converters. SiC detectors enable real-time estimation of secondary thermal neutron contributions, crucial for emerging radiotherapy techniques requiring precise neutron fluence monitoring. Beyond medical applications, the presented detectors show potential for neutron dosimetry, radiation monitoring, nuclear safety, and scientific research. The SiC diode active detection layer is less than 30 µm thick, and provides excellent gamma rejection, allowing discrimination of neutrons-induced events in mixed radiation fields. Experimental tests conducted on a TrueBeam radiotherapy LINAC demonstrated a thermal neutron detection efficiency of (4.32 ± 0.02)% for a (50 ± 10) µm thick LiF neutron converter. The detector, placed at 1.2 m from the accelerator isocenter, was used to measure neutron fluences at different monitor unit (MU) rates, ranging from 100 to 600 MU/min, with the LINAC operating at 15 MV. Under these conditions, the detector exhibited good linearity, without saturation or dead time effects.
Sci Rep 15, 30543 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-13052-w
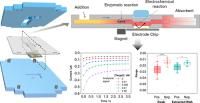
Providing viral load numbers of infection events aids in the identification of disease severity and in the effective overall patient management. Gold-standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques make this possible but cannot be applied at the point of need and in low-resource settings. Here, we report on the development of a compact analytical platform that can detect a conserved sequence of the RNA of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in 40 min in nasopharyngeal swab samples without the need for any previous purification or gene amplification steps. It combines electrochemical and paper fluidic approaches together with a sandwich hybridization assay performed on magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) modified with a tailor-designed capture DNA hairpin. The device proves to quantitatively detect viral RNA in a retrospective study carried out with nasopharyngeal swab samples. A sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 93% were estimated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. However, although molar concentration values of the target RNA sequence are provided, these estimates do not fully correlate with the viral load numbers estimated by RT-qPCR over the whole Ct sample range. Empirical studies have been carried out that have provided clear insights into this hurdle and simple solutions to overcome it, without depriving the device of the features required for potential use in a point-of-care (PoC) environment.
Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 22, 11863–11873. DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01605