Articles científics destacats
Aquesta secció inclou una llista dels treballs científics més destacats de l'IMB-CNM publicats en revistes incloses al Science Citation Index (SCI), per any de publicació.
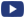
Several thermal management strategies for LED drivers designed for high lumen retrofit LED lamps are studied by simulation and experimentation means. Depending on the driver output, two scenarios are analyzed: Low Voltage-High Current (18V-620mA) and High Voltage-Low Current (110V-85mA). Experiments (infrared thermography and thermocouples) and multiscale simulation approaches are used to assist both the lamp and driver board thermal design, as well as the driver proper integration in the lighting system. As a result, a heatsink based on an Aluminum hollow cylinder with polymer axial fins is designed and evaluated. The heatsink assessement is carried out with an LED board, in which the LED junction temperature is modeled and extracted by monitoring the LED board backside temperature. Additional experimentation to better integrate the driver is performed aiming at reducing the contact thermal resistance between the driver and the heatsink and improving the heat removal in the driver housing by including a material with a high thermal conductivity (i.e., dry silica sand or magnesium oxide powder). The proposed solution reduces the LED junction temperature up to 18% with respect to a reference lamp, whereas both drivers depict working temperatures around or below 125°C, when a working temperature of 90°C is considered.
IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics.
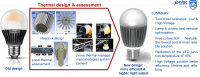
A novel impedance-based aptasensor for detection of E. coli O157:H7 is proposed. The limit of detection of the biosensor is around 102 cfu·mL-1 with a detection time of 30 minutes. The selectivity of the developed aptasensor is demonstrated in regard to other bacterial strains. Regeneration protocol for the aptasensor, to be employed more than once, has been developed
Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical V. 255 P3 (2018) pp. 2988-2995.

This paper focuses on providing an improved and efficient alternative to electromechanical relays (EMRs) in view of the growing demand characteristics for an effective power multiplexing in induction heating applications. A major analytical approach to the design and implementation of bidirectional switches (BDSs) based on different power semiconductor technologies is presented, including thorough static and dynamic characterizations. Emerging gallium nitride high-electron-mobility transistors (GaN HEMTs) and silicon carbide (SiC)-based devices are identified as potential candidates for the mentioned applications.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, vol. 66, no. 3, March 2019, pp. 1832-1841
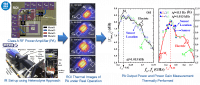
The viability of using off-chip single-shot imaging techniques for local thermal testing in integrated radio frequency (RF) power amplifiers (PAs) is analyzed. With this approach, the frequency response of the output power and power gain of a Class A RF PA is measured, also deriving information about the intrinsic operation of its transistors. To carry out this paper, the PA is heterodynally driven, and its electrical behavior is down converted into a lower frequency thermal field acquirable with an InfraRed lock-in thermography (IR-LIT) system. After discussing the theory, the feasibility of the proposed approach is demonstrated and assessed with thermal sensors monolithically integrated in the PA. As crucial advantages to RF-testing, this local approach is noninvasive and demands less complex instrumentation than the mainstream commercially available solutions.
IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1C (CPT1C) is implicated in central regulation of energy homeostasis. Our aim was to investigate whether CPT1C in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH) is involved in the activation of brown adipose tissue (BAT) thermogenesis in the early stages of diet-induced obesity.
Molecular Metabolism.

The paper shows that arrays of graphene microtransistors are used to record infraslow cortical brain activity. The devices may be useful for monitoring of brain physiology.
Nature Materials volume 18, pages 280–288 (2019).
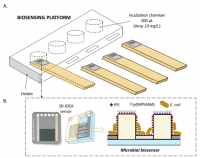
The developed microbial sensor based on interdigitated electrode array (3D-IDEA) impedimetric transducer was employed in a biosensing platform especially designed to monitor the bacterial response to the antibiotic ampicillin. To facilitate immobilization of bacteria within the trenches and prevent their deposition on top of the barriers an important novelty is the use of polyIJN-isopropylmethacrylamide) p(NIPMAM) microgels working as antifouling agents, deposited on top of the barriers by microcontact printing.
Lab. Chip, 2019, vol.19. pp. 1436 – 1447.
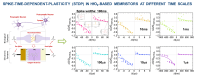
TiN/Ti/HfO2/W memristors have been investigated to mimic the spike-time dependent plasticity (STDP) of biological synapses at multiple time scales. For this purpose, a smart software tool has been implemented to control the instrumentation and to perform a dedicated ultra-fast pulsed characterization. Different time scales, from tens of milliseconds to hundreds of nanoseconds, have been explored to emulate the STDP learning rule in electronic synapses. The impact of such times on the synaptic weight potentiation and depression characteristics has also been discussed.
Microelectronic Engineering 215 (2019) 111014.

Modular microfluidic systems based on a new magnetic clamping approach, which enables both interconnection of microfluidic modules and reversible integration of solid-state sensors, is presented in this work. The system layout allows the easy assessment of the system fluidic performance by using optically transparent and low cost polymeric materials.
ACS Omega, 2019, 4 (4), pp 6192–6198.
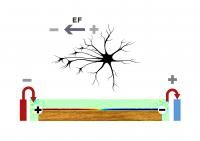
Implantable electrodes act with direct electrical contact although recent work has shown that electrostimulation is also possible through non-contact wireless settings, through the generation of dipoles at the borders of the material by bipolar electrochemistry. Finite element studies shown here with the same configuration that the experimental processes described, evidence voltage profiles in qualitative agreement with known bipolar effects, although with a clear difference between intercalation materials and metals. These observations may explain the differences in neural cell growth observed for various substrate material.
Electrochimica Acta