IMB-CNM technologies selected among the 100 with the greatest commercial potential of the CSIC
CSIC launches a catalog with its 100 most innovative and cutting-edge technologies available for licensing or collaborative projects. It includes four developments made at the Institute of Microelectronics in Barcelona.

A fish monitoring system, a method for selective deposition of thin films, a sensor for the detection of pollutants in water and a point-of-care device for the detection of biomarkers are the technologies of the Institute of Microelectronics of Barcelona selected by the CSIC for its catalog of 100 technologies with the greatest commercial potential.
On the occasion of World Intellectual Property Day, which is celebrated every year on April 26, the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), part of the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, presented a free catalog that compiles a hundred of its leading technologies in areas of knowledge such as agriculture, biotechnology, energy and humanities, among others. The technologies presented are at an advanced level of development, offer innovative approaches and offer advantages over those already commercialized, which places them in an outstanding position for their transfer to the market with the aim of contributing to the development of society.
IMB-CNM's mission is to contribute to the implementation of solutions based on micro and nanoelectronic technologies in industrial products. Therefore, it has a strong activity in technology transfer, which mainly includes the creation of spin-off companies and the development of patents. The technologies highlighted in the catalog are the following.
AEFishBit - Stress and metabolism monitoring system to improve fish production in fish farms
Category: Agriculture, Livestock and Marine Sciences
IMB-CNM and IATS
Differential compared to other technologies
AEFishBit is a system for remote monitoring and alerting of the state of fish in fish farms. It has no limitations on the size of the fish to be analyzed and can monitor individuals far from the surface, unlike current systems based on image analysis or acoustic telemetry that are very limited by the size of the fish and the depth at which it is located. The system is easy to remove and reusable, as it is located in the operculum of the fish. It has a small size and weight, not exceeding one gram. The system is transferable to other farm animals beyond the marine environment.
Application and benefit
Fish, like many other animals, behave abnormally in stressful situations. This negative environment is reflected in fish growth, regardless of food availability. This phenomenon causes large economic losses to fish farm producers. Hence the importance of achieving a standard of fish health and welfare.
New method for selective thin film deposition based on an array of self-aligned metallic masks
Category: Electronics
Differential compared to other technologies
Currently there are several techniques for deposition of thin layers of metals on dielectric materials, but all of them have some drawbacks related to the chemicals used. The proposed method allows the selective deposition of materials on microelectronic devices and substrates using evaporation and sputtering equipment. It also allows automatic and fast alignment of the substrate with the masks.
Application and benefit
Very useful in the remetallization of aluminum top contacts in power devices, to allow subsequent soldering, to establish contact on nanotube layered substrates and for the direct definition of tracks on ceramic substrates. Furthermore the method is suitable for applications where standard photolithographic processes are not possible.
Portable electrochemical sensor for direct detection of contaminants in water
Category: Materials and Environment
Differential compared to other technologies
The sensor allows the detection of contaminants in the area where the sample has been taken by personnel without specific training. The sample does not need prior processing steps, it can be deposited directly on the sensor. This avoids sample handling steps and the use of contaminating reagents.
Application and benefit
Versatile equipment validated for chemical oxygen demand, which allows the detection of organic contaminants, and has also been tested for the detection of heavy metals. It can be applied in water released in a wastewater treatment plant to reduce its environmental impact, and in companies such as meat companies to detect the release of pollutants, as well as in the environmental monitoring of rivers and lakes.
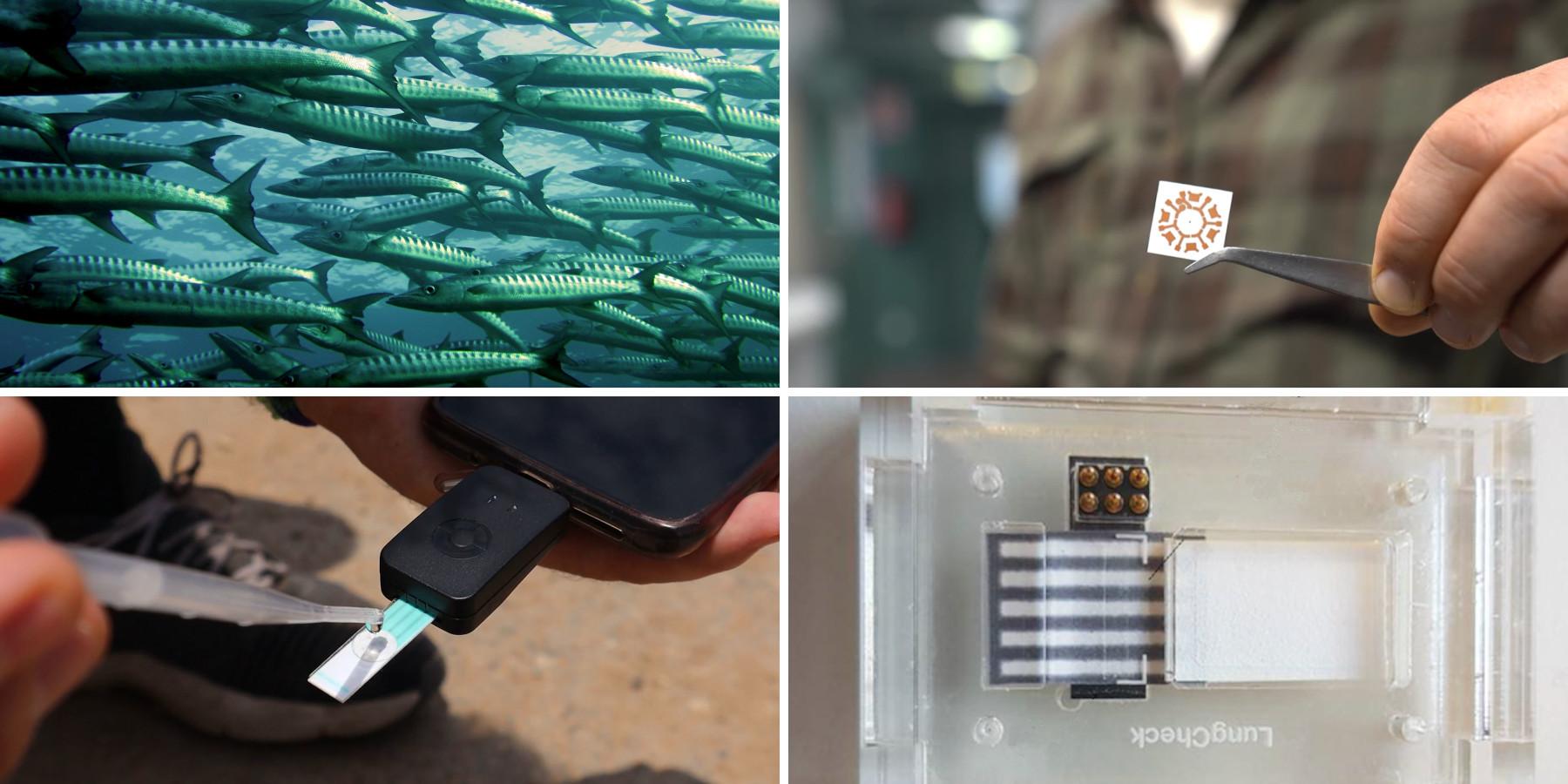
Point of Care microfluidic analytical device for rapid, multiplexed biomarker detection
Category: Health
Differential compared to other technologies
It is a low-cost technology, which has high sensitivity, allows rapid analysis and, in addition, minimizes residual material. It allows to obtain compact and simple devices to detect several parameters, whose number could be easily expanded without compromising the performance of the assay. This is suitable for
analyses such as those performed with ELISA sensors and so-called 'point of care' diagnostic devices, which are used in the same medical center as the patient and allow an immediate result to be obtained.
Application and benefit
The main advantages of the developed prototype are the possibility of simultaneous detection of biomarkers in blood, serum, urine, saliva, sputum, nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal samples. It can be applied for the detection of, for example, bacterial and viral proteins, such as those produced by SARS-CoV-2 infection, antibodies and cytokines, RNA, IgM and IgG (IL-6. IL-8).