Scientific Highlights
This section includes a list of the highlighted IMB-CNM scientific papers published in journals included in the Science Citation Index (SCI), per year of publication.
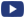
The aim of the present study was to combine the use of miniaturized and integrated impedimetric transducers and antimicrobial peptide AMPs to obtain biosensors with high sensitivity to monitor bacterial colonization to prevent implant-related infections.. Streptococcus sanguinis, which is one of the most prevalent strains in the onset of periodontal diseases, was used as a model of oral bacteria. To this end, a potent AMP derived from human lactoferrin was synthesized and covalently immobilized on interdigitated electrode arrays (IDEA). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were employed to optimize and characterize the method of immobilization.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics, vol. 86, 2016, pp.377-385.
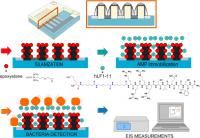
A new solid contact ion selective electrode with intermediate conducting polymer (CP) layer formed by electropolymerization on a gold electrode of a bifunctional monomer, n-phenyl-ethylenediaminemethacrylamide (NPEDMA), which contains a methacrylamide group attached to aniline, is presented. Ion-selective membrane based on acrylated urethane polymer was shown to co-polymerize with the CP forming highly adhesive boundary. The designed ion-selective electrode was successfully used for determination of total calcium ion concentration in blood serum samples.
Analytica Chimica Acta, vol. 943, 2016, pp. 50-57.

The development of an amperometric biosensor for L-malate determination showing long-term stability is reported in this work. The biosensor is based on a thin-film gold electrochemical transducer and a three-dimensional membrane of polypyrrole entrapping malate dehydrogenase and diaphorase enzymes. It was applied to monitor the malolactic fermentation of three red wines, showing a good agreement with the standard colorimetric method.
Anal. Chim. Acta 954 (2017) 105-113.
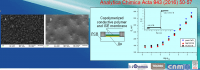
This paper studies by experimentation and physics-based simulation the Short-Circuit (SC) capability of several normally-off 600-650 V Gallium Nitride High-Electron-Mobility Transistors (GaN HEMTs): cascodes, p-GaN, and GaN Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor HEMTs (MISHEMTs). As a result, cascodes present the worst SC ruggedness. By contrast, p-GaN gate HEMTs and MISHEMTs provide a higher SC capability thanks to their strong drain current reduction. In addition, a valuable state-of-the-art about all commercially available technologies is also provided, which demonstrates that current GaN devices do not allow SC capability.
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 64 (11), pp. 9012-9022 (2017).
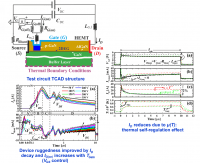
Gallium Nitride High-Electron-Mobility Transistors (GaN HEMTs) are promising devices for high-frequency and high-power density converters, but some of their applications (e.g., motor drives) require high robustness levels. In this scenario, 600 V normally-off p-GaN gate HEMTs are studied under short-circuit (SC) by experiment and physics-based simulations (drift-diffusion and thermodynamic models). As a main observation, a strong drain current reduction (> 70% after saturation peak) and high gate leakage current (tens of mA) are observed. All studied devices withstand the SC test at bus voltages up to 350 V, while fail at 400 V. Furthermore, its understanding is crucial to improving SC ruggedness in p-GaN HEMTs
IEEE Electron Device Letters, 38 (4), pp. 505-508 (2017).
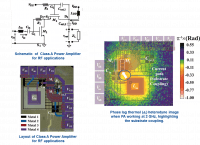
With thermal phase lag measurements, current paths are tracked in a Class A Radio Frequency (RF) power amplifier at 2 GHz. The phase lag maps evidence with a higher sensitivity than thermal amplitude measurements, an input-output loop due to a substrate capacitive coupling. This limits the amplifier’s performance, raising the power consumption in certain components. Other information relative to local power consumption and amplifier operation is also inferred. This approach allows the local non-invasive testing of integrated systems regardless of their operating frequency.
Appl. Phys. Lett., 101 (2) 094101 (2017).
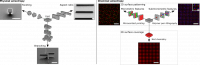
The physical and chemical properties of silicon chips can be tuned to address the requirements of the research. The control of the physical anisotropy from fabrication allows obtaining chips with the desired aspect ratio, branching, faceting and size. Subsequent surface modification via wet chemistry or contact printing added two- and 3-dimensional chemical features on each microparticle. The combination of physical and chemical anisotropies provides the mean to create a myriad of customized microparticles.
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017.
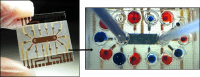
This work reports on the design, fabrication and performance of a low-cost, self-contained sampling device based on a wax microfluidics technology. This sampler delivers leak- and contamination-free performance that ensures the integrity of the collected samples. Thanks to its small dimensions and low power requirements, this device is well suited for collecting samples on-board of small aerial or aquatic drones.
Sensors and Actuators B 251 (2017) 93–98

An impedimetric sensor based on a three dimensional electrode array modified with consecutive deposition of Con A-glycogen-Con A layers was used for label-free detection of bacterial endotoxin: lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Escherichia coli. Presented biosensor is able to detect bacterial LPS in a very short detection time (20 min) with 2 μg mL−1 limit of detection, which is much lower than reported for other biosensors with Con A.
Electroquimica Acta, 2017, vol.243, pp.142-151

The impact of the dielectric thickness, forming polarity, and current compliance on the self-rectifying current–voltage characteristics of Ni/HfO2/n+-Si RRAM devices has been investigated. In the case of 5-nm-thick oxide devices, a self-rectifying ratio of three orders of magnitude is observed after substrate injection forming (SIF) with current compliance below 500 μA. However, devices subjected to gate injection forming (GIF) do not exhibit such rectifying feature. This distinctive behavior for SIF is ascribed to the formation of a Schottky-like contact in between the Ni-based conducting filament and the semiconductor electrode.
IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 64 (8) pp 3159-3166 (2017).