Scientific Highlights
This section includes a list of the highlighted IMB-CNM scientific papers published in journals included in the Science Citation Index (SCI), per year of publication.
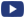
This work reports on the thermal influence of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) driver on a retrofit LED lamp, also reporting on a procedure for its thermal characterization and multi-scale modeling to optimise its integration. This study has been carried out within the Consumerizing Solid State Lighting project led by Philips and funded by ENIAC Joint Undertaking platform.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 30, NO. 7, JULY 2015

A photonic lab on a chip (PhLOC), comprising a solid-state light emitter (SSLE) aligned with a biofunctionalized optofluidic multiple internal reflection (MIR) system, is presented. The SSLE is obtained by filling a microfluidic structure with a phenyltrimethoxysilane (PhTMOS) aqueous sol solution containing a fluorophore organic dye. Its performance is assessed by measuring quinolone yellow, obtaining a limit of detection (LOD) of (0.60±0.01) µM. Finally, the MIR is selectively biofunctionalized with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) target analyte, obtaining a LOD of (0.7±0.1) µM for H2O2.
Light: Science & Applications (2015) 4, e271; DOI:10.1038/lsa.2015.44
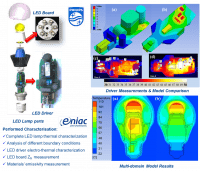
In this paper, we report on a method to reduce thin films of graphene oxide (GO) to a spatial resolution better than 100 nm over several tens of micrometers by means of an electrochemical scanning probe based lithography.
Nanotechnology 26 (2015) 285301.
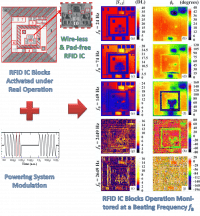
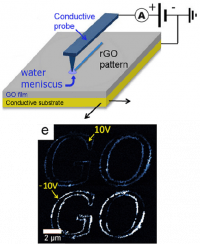
The functionality and consumption of an RFID IC supplied by Inductive Power Transfer (IPT) has been non-invasively analyzed by IR thermography.The main aspects addressed in thiswork have been: the suitability study of the proposed modulation strategies, the characterization of the coupling between coils and its effects on the RFID blocks, the RFID IC functional analysis, and the dependence of the local energy consumption on the total power delivered to the die.
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics
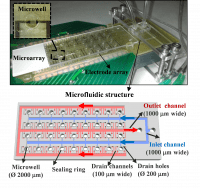
In this work an automated and reusable electrical readout system for low-cost glass slide microarrays is described. The system, which enabled the simultaneous conductimetric detection of up to 36 biorecognition events, comprises an array of interdigitated electrode transducers and a polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic structure, aligned over it.
The impedimetric system shows similar sensitivity to that of fluorescence scanners.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics 74 (2015) 698–704.
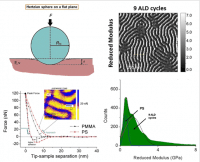
The mechanical properties of several types of block copolymer thin films have been investigated using PeakForce quantitative nanomechanical mapping. The samples consisted of polystyrene/poly(methylmethacrylate) with thickness below 50 nm and features of less than 22 nm.
Langmuir, 31 (2015) 11630
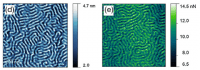
The nanomechanical properties of solvent-cast polymer thin films have been investigated using PeakForce™ Quantitative Nanomechanical Mapping. The samples consisted of films of polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate). Additionally, we have probed the mechanical properties of poly(styrene-b-methyl methacrylate) block copolymers (BCP) as randomly oriented thin films.
J. Micro/Nanolith. MEMS MOEMS 14 (2015) 033509.
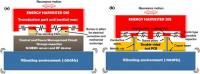
This work introduces a new concept to integrate energy-harvesting devices with the aim of improving their throughput, mainly in terms of scavenged energy density and frequency tunability. This concept, named energy harvester in package (EHiP), is focused on the heterogeneous integration of a MEMS die, dedicated to scavenging energy, with an auxiliary chip, which can include the control and power management circuitry, sensors and RF transmission capabilities. The main advantages are that the whole die can be used as an inertial mass and the chip area usage is optimized. An estimated maximum generated power of around 11 μW has been obtained for an input vibration acceleration of ∼10 m s−2 when the energy harvester operates in a constant-charge cycle for the best-case scenario.
Smart Mater. Struct. 24 (2015) 115027 (10pp).

Cone-like and empty cup-shaped nanoparticles of noble metals provide extraordinary optical properties for optical nanoantennas or nanoresonators. However, their large-scale production is difficult. We present a fabrication approach to achieve arrays of nanoparticles with tunable shape and composition by a combination of nanoimprint lithography, hard-mask definition and metal deposition.
The paper has been highlighted as a Nanotechnology Lab Talk: Mass producing tunable nanoparticles
Nanotechnology 26 (2015) 445302.
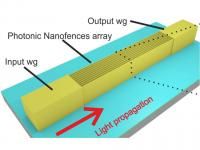
Photonic nanofences consisting of high aspect ratio polymeric optical subwavelength waveguides done by two-photon polymerization have shown extremely large evanescent field (70-90% of the total coupled light). This concept has been used for implementing an absorbance-based sensor for the determination of lead in water samples, obtaining a sensitivity of 0.102 AU/decade, and a linear range between 10-6 M and 10-2 M Pb(II) and a detection limit of 7.3 nM
ACS Nano, 2016, 10 (1), pp 778–785.